Recombinant Therapies: Transforming Healthcare and Tackling Chronic & Rare Diseases
In recent years, Recombinant Therapies have revolutionized the landscape of modern medicine, making remarkable strides in treating chronic and rare diseases. From diabetes to genetic disorders, these cutting-edge therapies offer more precise, effective, and safer alternatives compared to conventional treatments. They represent the pinnacle of Healthcare Innovations, and with ongoing advancements, they continue to reshape the future of medicine.
To fully grasp the significance of Recombinant Therapies, it is essential to understand the major differences between conventional products and recombinant products, how they are manufactured, and the profound impact they’ve had across various medical specialties.
Additionally, recent breakthroughs in Protein Therapeutics and Biopharmaceuticals underscore the power of these therapies in addressing some of the most complex health challenges today.
Differences Between Conventional and Recombinant Products
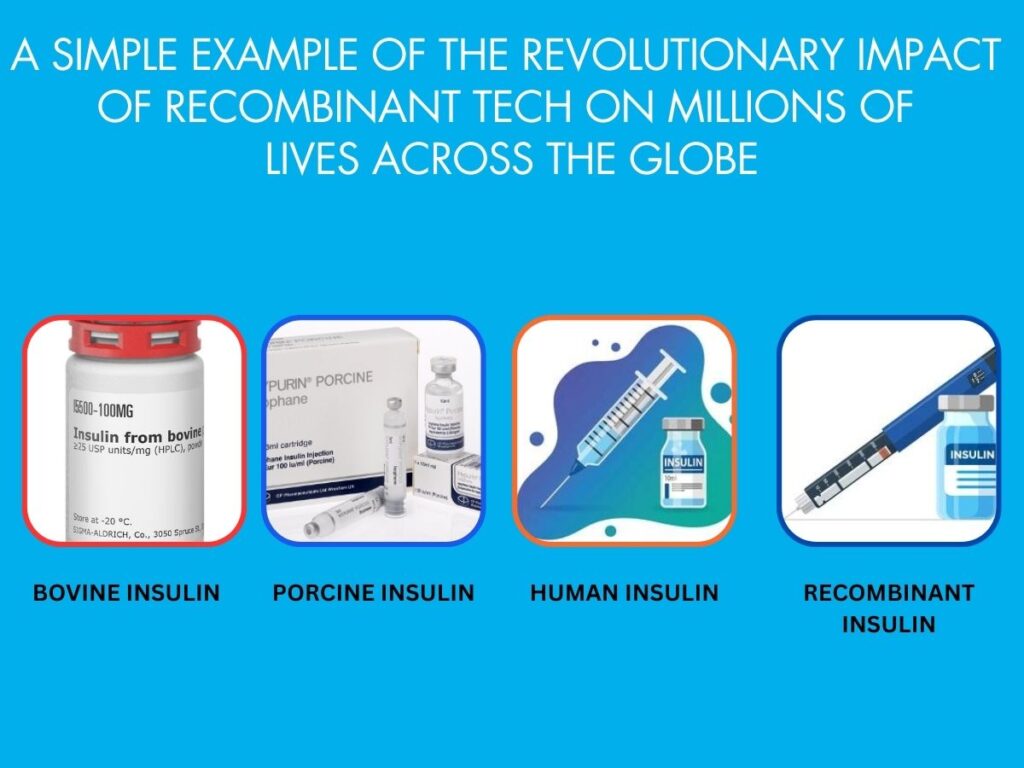
Conventional products rely on natural sources like animals, plants, or minerals. For instance, insulin used to be extracted from the pancreas of pigs (Porcine Insulin) or cows (Bovine Insulin). This process was limited in both availability and safety, as it could trigger immune responses in humans. Additionally, the scope of conventional treatments is limited since they typically involve using substances naturally available in biological systems, making mass production difficult.
I know of this first-hand, as I was part of a company marketing Bovine Insulin in India around the year 1998-99, which was being marketing as a very major breakthrough in scientific accomplishment in Diabetes management at that time, and that too with pathetic tolerance and unstable responses.
On the other hand now a days, Recombinant products are produced using genetic engineering techniques. In recombinant DNA technology, scientists insert specific genes into host cells (often bacteria or yeast) to produce the desired protein. These host cells can replicate rapidly and produce large quantities of the desired product.
For example, modern insulin is created using recombinant DNA, eliminating the need for animal sources and significantly improving both safety and efficacy. This Healthcare Innovation allows for producing precise proteins with minimal impurities and allergic reactions.
In short, Recombinant Therapies provide more precise, scalable, and safe alternatives to conventional products, making them the preferred choice for many modern treatments.
The Manufacturing Process: Conventional vs. Recombinant Products
The manufacturing process of conventional products is typically reliant on natural extraction. For example, blood-derived clotting factors used in hemophilia treatment were historically sourced from pooled human plasma, posing risks like viral contamination.
Conversely, recombinant manufacturing involves introducing human genes into microorganisms such as bacteria or yeast. These microorganisms are then cultured to produce large quantities of the required protein. The recombinant approach not only reduces the risk of contamination but also enhances scalability, purity, and precision. Modern Protein Therapeutics such as recombinant insulin or clotting factors are produced in controlled lab environments, ensuring they are more reliable, safer, and purer than their conventional counterparts.
This biotechnological process allows for precise control over the protein’s structure, ensuring high efficacy in targeting specific diseases. The ability to tailor-make these proteins has been a major leap forward in the development of Biopharmaceuticals, offering highly specialized treatments for chronic and rare diseases.
Medical Specialties Transformed by Recombinant Therapies
Recombinant products have made a profound impact across several medical specialties, delivering therapies that are far more effective than conventional treatments. Here are some key areas:
- Endocrinology: The most famous application of recombinant therapy is in diabetes treatment. The development of recombinant insulin revolutionized diabetes management, providing safer and more effective treatment than animal-derived insulin. Recombinant insulin reduces the risk of allergic reactions and offers precise control over blood sugar levels.
- Hematology: Patients with hemophilia have benefited immensely from Recombinant Therapies. Traditional clotting factors sourced from human plasma carried risks of viral contamination. Recombinant clotting factors, however, are produced in a controlled environment, significantly lowering the risk of infection and improving safety.
- Oncology: Protein Therapeutics like monoclonal antibodies are used in cancer treatment to target specific proteins on cancer cells, sparing healthy cells. These targeted therapies offer more effective cancer treatment options, often with fewer side effects compared to conventional chemotherapy.
- Genetics: Rare genetic disorders, which were once untreatable, now benefit from Recombinant Therapies. For example, enzyme replacement therapies (ERT) for conditions like Gaucher’s disease or Fabry disease are produced using recombinant DNA technology, offering patients life-saving treatments that weren’t available before.
- Immunology: Recombinant products like interferons and interleukins are used to modulate the immune system in diseases like multiple sclerosis and certain types of hepatitis. These therapies are more refined and targeted compared to conventional immune therapies.
Breakthroughs in Recombinant Therapies and Healthcare Innovations
Recent advancements in Recombinant Therapies have accelerated the pace of Healthcare Innovations, particularly in Protein Therapeutics and Biopharmaceuticals. Some notable breakthroughs include:
- CRISPR and Gene Editing: CRISPR technology, which enables precise gene editing, has enhanced the development of recombinant therapies. This technology allows for the correction of genetic defects at the DNA level, offering hope for curing genetic disorders like cystic fibrosis and muscular dystrophy.
- Monoclonal Antibodies: Recombinant monoclonal antibodies have become a staple in cancer treatment. These antibodies can be engineered to recognize and bind to specific proteins on cancer cells, marking them for destruction by the immune system. This approach is more targeted and has fewer side effects compared to traditional chemotherapy.
- Cell and Gene Therapies: Recombinant technologies are at the heart of new cell and gene therapies, such as CAR-T therapy, which engineers a patient’s own immune cells to fight cancer. These therapies are transforming how doctors treat previously untreatable conditions, offering new hope for patients with chronic and rare diseases.
- Protein-Based Vaccines: With the recent development of recombinant protein vaccines, such as those used in the fight against COVID-19, healthcare has seen massive advancements in preventing and controlling viral outbreaks. These vaccines are safer and easier to produce compared to traditional methods.
The Future of Recombinant Therapies: What’s Next?
The field of Recombinant Therapies is constantly evolving, and the next few years promise to bring even more significant advancements. Researchers are working to expand the use of recombinant products in treating a wider range of chronic and rare diseases. Some of the exciting areas of development include:
- Personalized Medicine: Using recombinant DNA technology, therapies can be tailored to an individual’s genetic makeup. This personalized approach will ensure that treatments are more effective, thereby reducing the risk of adverse reactions and improving outcomes for patients.
- Regenerative Medicine: Recombinant products are also being explored for use in regenerative medicine, where damaged tissues and organs can be repaired or even replaced using lab-grown proteins and cells.
- More Accessible Treatments: As Healthcare Innovations continue, the cost of producing Biopharmaceuticals may decrease, making advanced therapies more accessible to a broader population. This will be particularly beneficial for patients with rare diseases, many of whom have limited treatment options.
- Advanced Cancer Treatments: With the rapid development of monoclonal antibodies and CAR-T therapies, cancer treatment is likely to become even more targeted and effective, offering patients better survival rates and improved quality of life.
FAQs
- What are Recombinant Therapies? Recombinant therapies involve using genetically engineered products, typically proteins, to treat diseases. These therapies are produced by inserting specific human genes into microorganisms, which then produce the desired proteins.
- How are Recombinant products different from conventional products? Conventional products are typically derived from natural sources like animals or plants, whereas recombinant products are produced using genetic engineering techniques, making them safer, purer, and more scalable.
- Which diseases can be treated with Recombinant Therapies? Recombinant therapies are used to treat a wide range of diseases, including diabetes, cancer, hemophilia, and rare genetic disorders.
- What role do Protein Therapeutics play in Recombinant Therapies? Protein Therapeutics, such as monoclonal antibodies, play a crucial role in targeting specific diseases with high precision. These therapies are highly effective in treating conditions like cancer and autoimmune disorders.
- What are the advantages of Biopharmaceuticals produced through recombinant technology? Biopharmaceuticals produced through recombinant technology are more precise, safer, and can be tailored to treat specific diseases. They offer fewer side effects and are manufactured in controlled environments, reducing contamination risks.
Conclusion
Recombinant Therapies represent a true revolution in the field of medicine. By harnessing the power of genetic engineering, scientists have developed highly effective, precise treatments for chronic and rare diseases.
The recent breakthroughs in Healthcare Innovations, Protein Therapeutics, and Biopharmaceuticals are transforming how we approach healthcare, providing hope for patients who previously had limited or no treatment options.
As the field continues to advance, the future of recombinant products holds the promise of even more impactful therapies, ultimately improving the quality of life for countless individuals worldwide.
